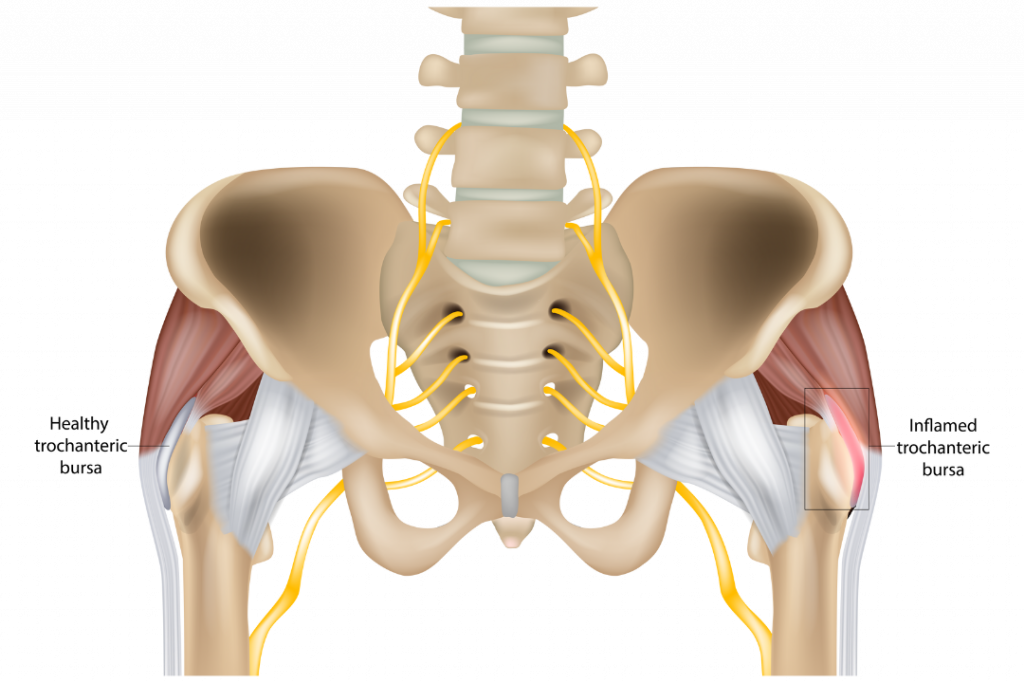
Hip bursitis is a painful condition that occurs when the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs become inflamed. These sacs cushion the bones, muscles, and tendons around the hip joint. The hip joint is the largest joint in the body, and bursae are located in various areas around the hip. This includes the greater trochanter, which is the bony bump on the outside of the hip. Read on to find out what is hip bursitis and how you can treat it?
Who gets hip bursitis?
Hip bursitis is most commonly seen in middle-aged or older adults, and is more prevalent in women than men. It can also be seen in athletes or individuals who engage in activities that involve repetitive movements of the hip. Activities such as running or cycling. Other risk factors include previous hip surgery, hip arthritis, and spinal conditions that affect the lower back and hip area.
What causes hip bursitis?
The exact cause of hip bursitis is not always clear. However, it is thought to be caused by repetitive stress or overuse of the hip joint. It can also be caused by an injury to the hip, such as a fall or direct blow to the hip area. Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and gout, can also increase the risk of developing hip bursitis.
Hip bursitis can cause pain and tenderness on the outer part of the hip. This may worsen with prolonged periods of standing, walking, or climbing stairs. The affected area may also be swollen and red. In severe cases, the pain can affect a person’s ability to walk or perform daily activities.
What is the treatment?
Treatment for hip bursitis typically involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, and medication. Resting the affected hip can help to reduce inflammation and pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroid injections can be used to reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapy such as remedial massage, dry needling and TENS can be helpful in improving hip flexibility and strength, which can also help to reduce pain and prevent future injuries.
In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the inflamed bursa or to repair any damage to the hip joint. However, surgery is typically reserved for cases that do not respond to conservative treatment methods.
Self care for hip bursitis
Stretching is an essential part of treating hip bursitis, as it helps to improve flexibility and range of motion in the hip joint. Here are some stretches that can be helpful for relieving hip bursitis:
Hip Flexor Stretch: Kneel or lunge on one knee, with the other foot flat on the ground in front of you. Lean forward and press your hips forward until you feel a stretch in the front of the hip of the kneeling leg. Hold for 30 seconds and repeat on the other side.
Piriformis Stretch: Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the ground. Cross one ankle over the opposite knee, and pull the other knee toward your chest. Hold for 30 seconds and repeat on the other side.
Clam shells: Lie on your side with your feet, ankles and knees together. Bend the legs a little and tighten your core stability muscles. Keeping the feet together, lift the top knee up.
Make sure you don’t roll your body back with the movement. Control the movement as you bring the knee back down to the starting position.
Quadriceps stretch: Start in a standing position. Use a desk or chair for support, and raise one leg behind you grabbing hold of your ankle, or your lower leg. Lift your leg as high as possible and keeping your torso upright and knees together. Hold for a few seconds, and then repeat for the other leg. A belt or towel wrapped around the foot can be used to assist the stretch.
It’s important to remember to stretch gently and not force any stretches beyond what feels comfortable. If you experience pain or discomfort during any of these stretches, stop immediately and consult with your healthcare provider. Additionally, it’s always a good idea to consult with your physical therapist or healthcare provider before beginning any new stretching or exercise routine.
In conclusion, hip bursitis is a painful condition that can be caused by repetitive stress or overuse of the hip joint. It is more commonly seen in middle-aged or older adults, and is more prevalent in women than men. Treatment typically involves rest, physical therapy, and medication, and in severe cases, surgery may be necessary. If you are experiencing hip pain or have been diagnosed with hip bursitis, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for your specific needs.